What is a Jaw Cyst?
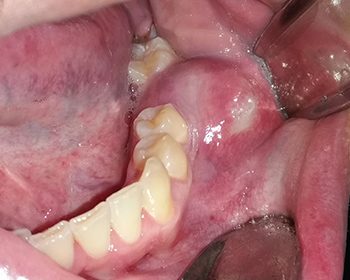
Jaw cysts are pathological formations, which occur for different reasons and require surgical intervention. Cavities in different sizes located in the soft tissue, which are filled with fluid or air, and which are enclosed in a thin membrane that separates them from the surrounding healthy tissue and bone in the oral region, are called cysts.
They usually manifest themselves with pain or swelling. However, there are also cysts that reach various sizes without being noticed.
Although jaw cysts are defined as benign formations, intervention may be needed depending on the situation. Cysts not operated despite the need for surgical intervention may cause deformation or malignant tumors on the jawbone.
How Is A Jaw Cyst Removal Surgery Performed?
Jaw cysts are removed painlessly under local anesthesia. There are some medications you should take and some rules you should comply with after surgery. It basically does not differ from tooth extraction or implant placement procedures. After surgery, it is of great importance to pay attention to oral hygiene, to use the medications prescribed on time, and to go for periodic checkups regularly. However, the operated are should not be exposed to any trauma or pressure. After jaw cyst surgery, patients should go for periodic checkups once a year.
Jaw cysts, which are usually filled with fluid, develop in the bone and soft tissue in the jaw area. These cysts tend to grow with the increase of fluid pressure inside them and carry the risk of infection. With the infection, swelling and pain begin to seriously discomfort the patient. Jaw cysts, which are generally detected by imaging techniques, can also manifest themselves with numbness and extraoral swelling in the lips in advanced cases. Periodontal problems and untreated dental caries are the leading factors for the formation of jaw cysts. Conditions such as neglected tooth decay, poor oral hygiene, and untreated intraoral infections considerably threaten the jawbone and soft tissue and adversely affect the general state of health. Jaw cysts are sometimes detected during a routine dental examination, although they cause no symptom. For these reasons, everyone must visit a dentist at least once a year.


